

Batteries contain many toxic materials such as cadmium, mercury, lead and lithium. These materials are non-renewable and can be recycled an indefinite amount of times. When these liquids or metals are exposed it can poison the health of many animals and people, in addition to contaminating body’s of water, soils and can cause pollution in the air. It is also partly responsible for global warming, as the manufacture and transportation of batteries emit exhaust and other pollutants into the atmosphere. Heavy metals such as cadmium and lead both contribute to the toxicity of biological molecules, hence leading to many adverse effects on the body. An example these poisonous metals such as nickel and cadmium (carcinogens) can cause are cancer, neurological damage, liver and lung disease. Mercury is a highly toxic chemical compound in its vapor for and can cause paralysis and psychosis. Lead has been linked to birth defects, and to neurological and developmental damage.


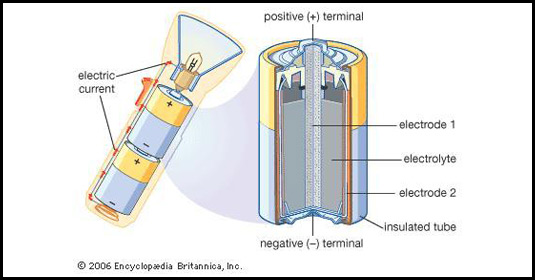

Lithium is responsible for landfill fires that can burn underground for years, releasing toxic chemicals into the air, and increasing the potential for human exposure. Pollutants like these can leak as the battery corrodes causing major damaging long-term effects towards our environment. It can effect food chains, contaminate landfills and overheat leading to fires. In most parts of the world, household batteries are dumped into landfills, incinerators or the ocean. All affecting multiple life forms, ecosystems and organisms across the planet, poisoning them. Recycling these batteries can help prevent these hazards simply by just covering the ends with tape, or distancing the batteries from each other and other recyclable products like plastic and cardboard. In conclusion all batteries should be handled with care as depending on the type where they can be more or less toxic.
© copyright 2022 by Recycle My Battery